EAST AFRICAN LANDSCAPES UNDER THE EWT/INTERNATIONAL CRANE FOUNDATION PARTNERSHIP
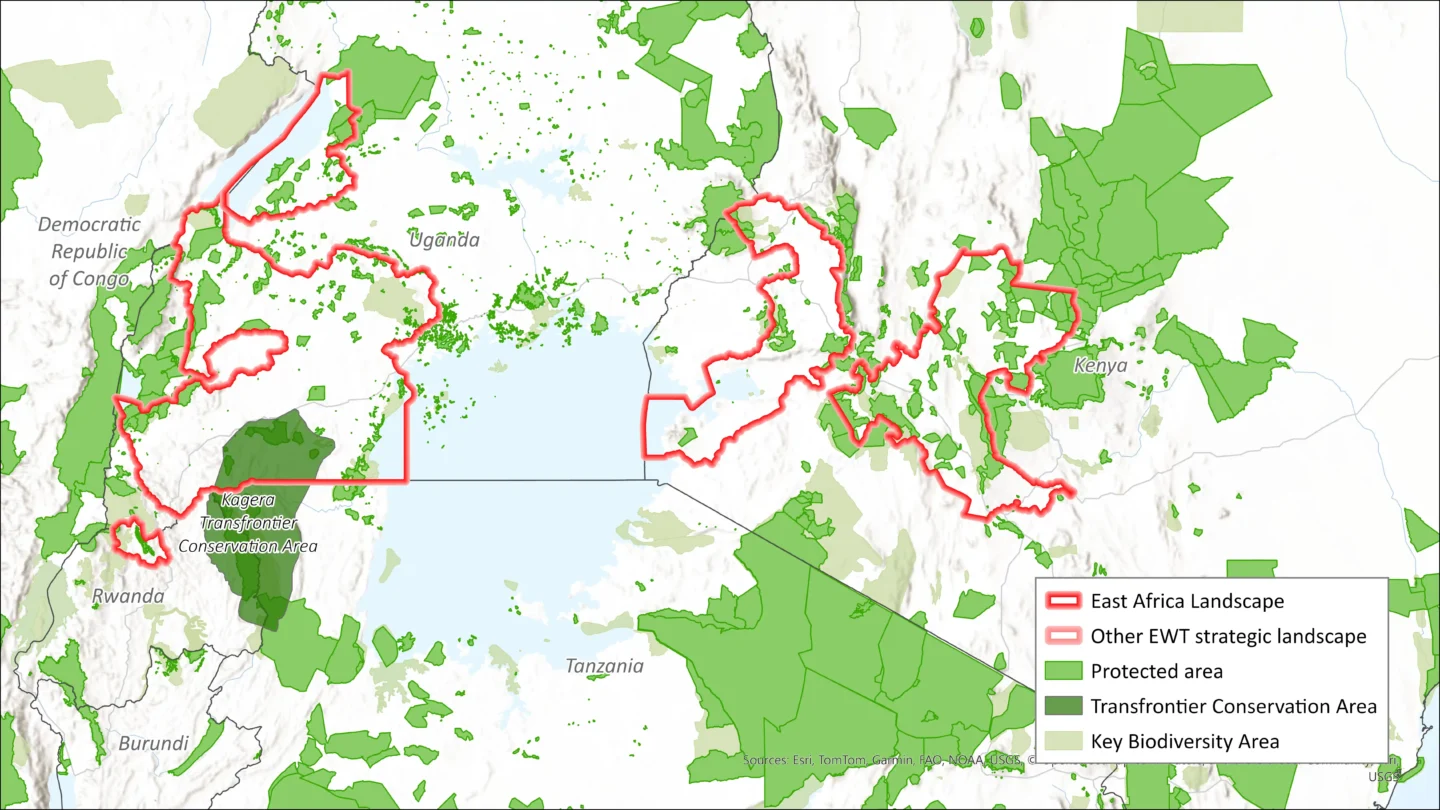 The East Africa Crane Conservation Landscape focuses on high-altitude wetlands and grasslands across countries like Uganda, Rwanda, Kenya, and Ethiopia. These fragile ecosystems support some of the last strongholds for species like the Grey Crowned Crane and the Wattled Crane – birds deeply rooted in local culture and closely tied to healthy wetland systems. These areas also provide clean water, grazing, and fertile soils that sustain surrounding communities.
The East Africa Crane Conservation Landscape focuses on high-altitude wetlands and grasslands across countries like Uganda, Rwanda, Kenya, and Ethiopia. These fragile ecosystems support some of the last strongholds for species like the Grey Crowned Crane and the Wattled Crane – birds deeply rooted in local culture and closely tied to healthy wetland systems. These areas also provide clean water, grazing, and fertile soils that sustain surrounding communities.
The EWT/ICF Partnership works in this landscape to protect crane populations while supporting the people who live alongside them. We partner with communities to reduce illegal trade, restore wetland habitats, and strengthen local awareness around the importance of crane conservation. Our approach connects species recovery with improved land stewardship, helping people manage water and grazing in ways that support both biodiversity and livelihoods.
To make these efforts sustainable, we are developing finance models that support local conservation leadership and help fund long-term restoration. We’re also working to ensure that infrastructure development considers the needs of cranes and wetland habitats. Bioblitzes and other research tools are helping us map crane populations, identify new threats, and guide targeted action.
This is a landscape where the future of some of Africa’s most iconic birds depends on people’s ability to live well with nature. Through shared action and long-term commitment, we are working to protect these wetlands, secure healthy crane populations, and support people in shaping a more sustainable future.
Why it’s important
The East Africa Strategic Conservation Landscape is vital to the EWTs strategy for its biodiversity and its role in protecting Grey Crowned Crane populations through wetland habitats and migratory routes.
This landscape is crucial not only for wildlife, but also for local communities who depend on these wetlands for agriculture and resources. By promoting sustainable land use and community-based conservation, it fosters coexistence between people and wildlife.
However, the landscape faces threats from habitat loss, wetland drainage, and illegal wildlife trade. Urgent action is needed to preserve both the Grey Crowned Crane and the essential ecological services these wetlands provide, such as water purification, climate regulation, and food security.
Protecting this landscape is critical for maintaining both the region’s ecological balance and the livelihoods of people who rely on its resources.
So What?
Losing the East Africa Strategic Conservation Landscape would mean more than the extinction of an iconic bird, it would dismantle a vital natural system that filters water, buffers communities against climate impacts, and sustains rural economies.
These wetlands are not just habitats; they are food baskets, water towers, and cultural touchstones. The cost of inaction will be ecological, yes – but it will also be social and economic, undermining both biodiversity and the wellbeing of communities across the region.
Urgent, long-term investment in conservation is a direct investment in a more stable, sustainable future for East Africa.
Vision
Ensure that the Grey Crowned Crane populations in East Africa (Uganda, Kenya, and Rwanda) are stable or increasing, have sufficient high-quality habitat, and that communities sharing landscapes with cranes have resilient livelihoods.
Target Species
Landscape Size
90,996 KM²
Why we do it

protect biodiveristy
Lead collaborative efforts to safeguard species and rebuild life-sustaining ecosystems, working with, for example, governments, landowners, and Indigenous Peoples and Local Communities (IPLCs).

secure vital ecosystem services
Healthy ecosystems provide essential services like clean air, water, and food security.

Empower communities
Enable IPLCs to thrive through nature-based solutions that connect conservation with human well-being, equity, and sustainable livelihoods.

build a sustainable future
Embed biodiversity into corporate strategies and operations to deliver measurable positive outcomes for nature and create resilient, future-fit businesses.

Improve climate Resilience
Build climate adaptation and resilience into conservation efforts to protect biodiversity and human well-being.

Enhance water security
Prioritise the safeguarding of critical freshwater systems and catchments across Africa's threatened landscapes.
Cross cutting approaches

People in conservation unit
Co-developing and implementing conservation management approaches to ensure sustainable conservation impact and benefit sharing.

Wildlife and Infrastructure unit
Reducing infrastructure impacts on species and habitats.

Biodiversity and Business Unit
Supporting the integration of biodiversity into corporate strategy and operations, to achieve measurable positive biodiversity outcomes.

Sustainable Finance Unit
Focusing on mobilising financial resources to support conservation efforts.

Wildlife in Trade Unit
Disrupting and preventing illegal wildlife trade in the landscape.

Conservation Tools and Technology Unit
Discovering new species and understanding species distributions to inform conservation priorities in the landscape.
